[2] Add Two Numbers
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
复杂的数据结构是我的超级短板. 但是也算勉强看懂了js是如何表示链表的.
1 | /** |
[21] Merge Two Sorted Lists
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new sorted list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
解题的重点在于, 一直将l1和l2的链表头作比较, 不断将较小的node加入结果链表, 直至l1或者l2为空, 说明遍历结束. 把不为空的链表剩余的部分直接接入结果列表.
1 | var mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) { |
[24] Swap Nodes in Pairs
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
在交换链表的时候, 第一次交换需要记住链表头.
确定 curr 之后, 只有 curr.next!=null 时才有交换的必要, 否则说明交换到头了, 返回 head 即可.
1 | /** |
[61] Rotate List
Given a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
1 | /** |
[23] Merge k Sorted Lists
You are given an array of
klinked-listslists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order.Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it.
solution1 的时间复杂度分析:
时间复杂度: 遍历链表+排序+遍历数组
假设总node数为 $N$ , 则总时间复杂度为 $O(N)+O(NlogN)+O(N)=O(N)$
空间复杂度为: $O(N)$ , 主要是存储节点的数组的消耗
solution2 的时间复杂度分析:
设k=lists.length, $N$ 为所有节点数, 则复杂度为=归并次数每一次归并的时间复杂度
每一次归并需要遍历所有的节点, 但是不需要排序, 仅仅是大小比较, $O(N)$
设一共归并的次数为x, 则有 $2^x = k$ , 则 $ x = \log_2 k$ (以2为底k的对数)
所以总共的时间复杂度是 $\sum_0^x O(N)=O(N\log k)$
1 | // solution 1 |
[25] Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
时间复杂度分析:
$O(N)$ , $N$为链表总节点数, 翻转时需要遍历所有的节点. 一共会进行$\lfloor N/k \rfloor$ 次翻转, 每一次翻转需要$O(k)$的时间.
空间复杂度: 常量级别.
1 | // 大体思路是 每k个元素进行一次翻转 |
[83] Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once.
思路比较简单, 由于最坏情况是遍历链表的所有节点(当所有节点的值均不相同), 时间复杂度为 $O(N)$ .
1 | // 由于是排过序的链表 |
[82] Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
Given a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list.
Return the linked list sorted as well.
遍历链表的所有节点两次, 时间复杂度为 $2*O(N) = O(N)$ .
1 | // 遍历两次链表 |
[142] Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return
null.There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the
nextpointer. Internally,posis used to denote the index of the node that tail’snextpointer is connected to. Note thatposis not passed as a parameter.Notice that you should not modify the linked list.
这里需要证明下有环情况下, 为什么快慢指针第一次相遇之后, 快指针到链表头, 再和慢指针一起以每次一步的速度前进, 当二者相等时, 即是环的起点.
证明:
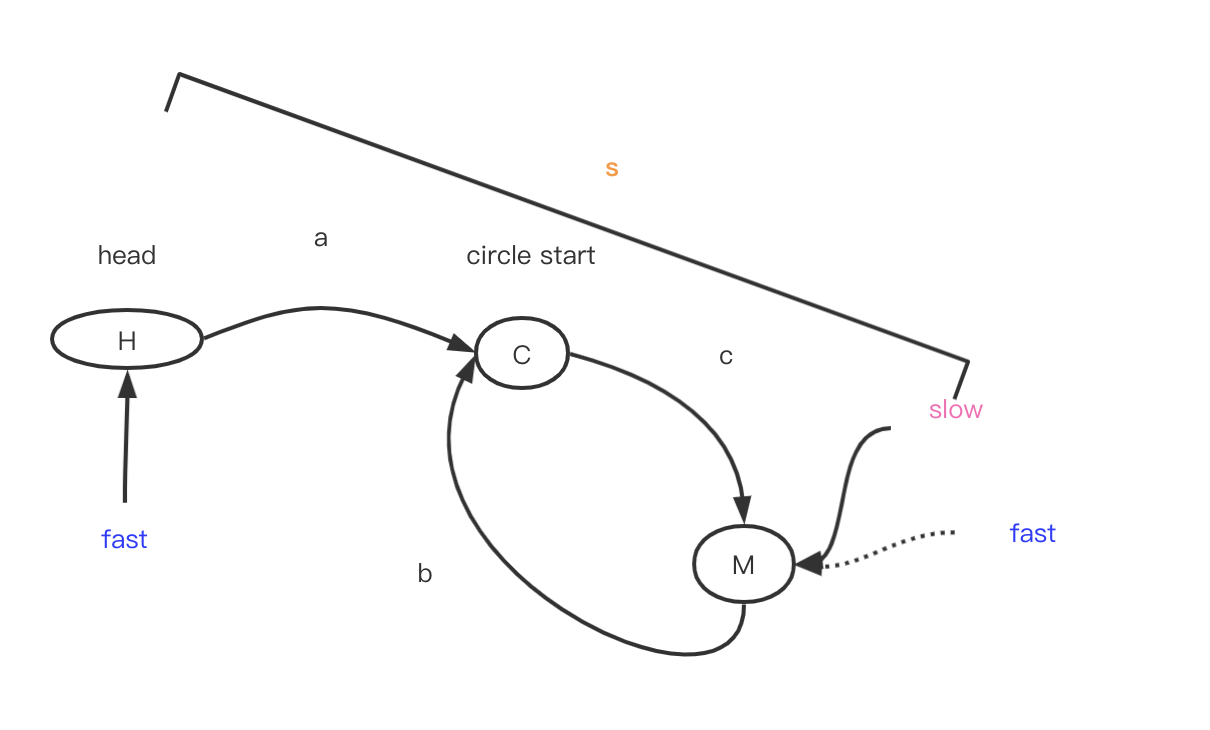
我们最终需要证明a=b. 假设链表总长度为L, 环的长度为R, 快慢指针第一次相遇的节点为M, 环的开始节点为C, 其中各个点之间的距离分别为 H->C=a, C->M=c, M->C=b, H->M=s. 第一次相遇时, 假设fast已经围绕着环走了n圈, 则有:
由于快慢指针的速度差两倍, 所以相同时间内, 快指针走过的距离是慢指针的两倍.
$2s = s + nR \-> s = nR \tag{1}$
已知慢指针走的长度为(套用$(1)$):
$a+c = s \-> a+c=nR \-> a + c = (n-1)R + R \-> a = (n-1)R + (R - c) \-> a = (n-1)R +b$
则得出结论 $a=b$, (这个还要再想下).
所以fast移动到head, slow位置不变, 两个同时开始走, 每次走一步, 当走了a步时,两者相遇的点即为环的起点.
时间复杂度:
可知快慢指针走的步数是一样的, 只是一个快一个慢, 慢指针最后遍历了整个链表, 走了N步, 则快指针也走了N步, 则时间复杂度为: $2*O(N)= O(N)$.
1 | // 使用快慢指针 |
[138] Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of
nnodes. Each node is represented as a pair of[val, random_index]where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
时间复杂度: 遍历两遍数组 $O(N)$.
经验/收获:
- 一开始我的问题在于试错, 都没有搞清楚
random_index属性是否在题目给的链表结构中存在, 我还以为有random_index这个属性呢, 实际上没有.random数据类型仍然是指针而非number. - 搞清楚题目是深拷贝, 不能改变原有链表结构. 需要重新生成新链表.
- 收获在于知道如何使用hashMap存储链表间的 links.
1 | // 题目要求是深拷贝 |
[92] Reverse Linked List II
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
时间复杂度分析:
假设链表总长度为$N$, 在定位m/n节点的过程中, 一共遍历链表一次, 每次遍历至第n个节点, 最差情况遍历到链表末尾.
翻转时一共需要翻转 $n-m+1$ 个节点, 需要的时间是 $ O(n-m+1)$ .
所以时间复杂度为 $O(N)$
注意:
初始化一个节点时, hair不是空, hair.val是空. 刚开始判断pre==null就写错了, 应该是pre.val是否null.
1 | var reverseBetween = function (head, m, n) { |
[147] Insertion Sort List
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.
时间复杂度分析:
遍历链表一次, $O(N)$
每到链表的一个节点, 就会扫描排好序的链表部分, 时间为 $O(1)+O(2)+O(3)+…+O(N-1)$
则时间复杂度为: $O(1)+O(2)+…+O(N)=O((N^2+N)/2)=O(N^2)$
1 | // 使用插入排序对链表进行排序 |
[203] Remove Linked List Elements
Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value val\.
时间复杂度: 遍历链表 $O(N)$
1 | var removeElements = function (head, val) { |
[206] Reverse Linked List
Reverse a singly linked list.
Follow up:
A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
递归过程需要详细的过程分析图(TO DO).
两种时间复杂度均为 $O(N)$.
递归方法的时间复杂度分析: 遍历整个链表, 递归调用N次.
1 | // 迭代翻转 |
[237] Delete Node in a Linked List
Write a function to delete a node in a singly-linked list. You will not be given access to the
headof the list, instead you will be given access to the node to be deleted directly.It is guaranteed that the node to be deleted is not a tail node in the list.
注意看题目条件, 时间/空间复杂度均为 $O(N)$.
1 | // 一时没有想起来用什么解法 |
[234] Palindrome Linked List
Given a singly linked list, determine if it is a palindrome.
Follow up:
Could you do it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
时间复杂度:
遍历链表一次, $O(N)$, 后半部分翻转链表的时候, 时间为$O(N/2)$.
所以时间复杂度为: $O(N)+O(N/2)=O(N)$.
方法:
判断回文链表,要求只能遍历一次链表.
将链表后半段翻转 再将前后部分分别比较.
然后还有需要注意的是: 快慢指针法寻找链表中心点
1 | var isPalindrome = function (head) { |
[160] Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null.- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Each value on each linked list is in the range
[1, 10^9].- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
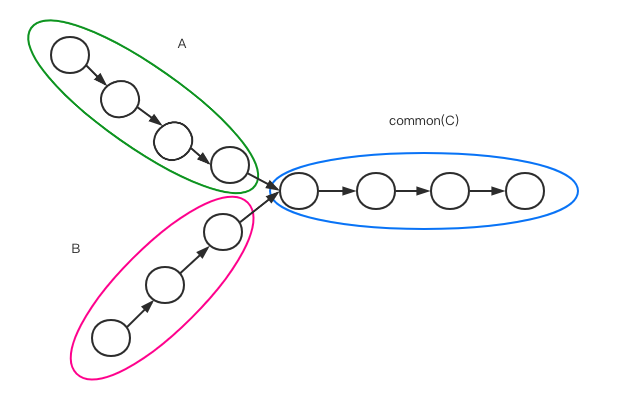
由图可知:
$headA = A + C$
$headB = B + C$
所以:
$newA = headA + headB = A + C + B + C$
$newB = headB + headA = B + C + A + C$
已知:
$A + C + B = B + C + A$
所以 newA与newB同时出发, 每次都走一步.
newA走完headA再走完B, newB走完headB再走完A, 如果两者有交点, 则此时会相等且不为null;
如果不相交, 则走到最后两者也相等, 但是为null.
时间复杂度:
假设headA和headB总共的长度为N, 则一共遍历了两次, 时间为$2*O(N)$, 时间复杂度为$O(N)$.
1 | // 思路很巧妙 需要分析下 最后两个节点一定会相等 |
[328] Odd Even Linked List
Given a singly linked list, group all odd nodes together followed by the even nodes. Please note here we are talking about the node number and not the value in the nodes.
You should try to do it in place. The program should run in O(1) space complexity and O(nodes) time complexity.
时间复杂度: 两个指针同时遍历, 一共遍历一遍链表. $O(N)$
空间复杂度: 只是新建了两个指针, 改动原有链表, 没有重新生成head的copy版本. $O(1)$
1 | // 完全自己想的法子 太棒了 |
[725] Split Linked List in Parts
Given a (singly) linked list with head node
root, write a function to split the linked list intokconsecutive linked list “parts”.The length of each part should be as equal as possible: no two parts should have a size differing by more than 1. This may lead to some parts being null.
The parts should be in order of occurrence in the input list, and parts occurring earlier should always have a size greater than or equal parts occurring later.
Return a List of ListNode’s representing the linked list parts that are formed.
Examples 1->2->3->4, k = 5 // 5 equal parts [ [1], [2], [3], [4], null ]
理解题意 一共分为 k 部分 而不是长度是 k !!
时间复杂度*:
在计算链表长度时, 遍历了一次. 后面将链表片段加入时, 又遍历了一遍.
所以时间复杂度为 $O(N+k)$, 在k>len时, 需要继续向结果中加入片段.
空间复杂度:
生成answer时res数组中包含的节点个数, k>len, k个链表节点, 反之, len个链表节点. 所以空间复杂度为$O(max(N, k))$.
1 | var splitListToParts = function (root, k) { |
[445] Add Two Numbers II
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Follow up:
What if you cannot modify the input lists? In other words, reversing the lists is not allowed.
题目要求不能翻转链表, 于是遍历链表, 将链表中的数都存进栈中. 再通过将栈弹出, 进行相加操作.
时间复杂度:
遍历两个链表, O(N). 两个栈均弹出进行相加操作, O(N). 因此时间为 $2O(N)=O(N)$
空间复杂度:
使用两个栈存储数字, O(N), 相加之后得到新的结果列表的长度 O(max(m, n)) ps.是两个链表中较长的那一个Lmax, 结果链表长度可能由于进位问题会是Lmax+1, 因此空间复杂度为 $O(N)+O(max(m, n))$.
1 | // 不能够翻转链表 |